Fabrication is an important element in the manufacturing world. Fabrication plays a vital role in building construction structures and developing consumer goods, machines, and more. However, before diving into the fabrication processes in manufacturing, let us first understand fabrication in manufacturing.
What is Fabrication in Manufacturing?
Fabrication in manufacturing refers to constructing elements or products from raw materials. This involves several techniques, which help accelerate the entire process. This process is used in automotive, construction, electrical, aerospace, and more industries. Fabrication shapes and transforms metals such as plastic, steel, and others into desired products or components using certain techniques. The goal of fabrication is to build durable and high-end products by using cost-effective methods. This is one of the modern industrial processes that plays a major role in contributing to industry innovation and advancements in technology and other diverse areas.
Top 5 Fabrication Techniques
1.) Cutting
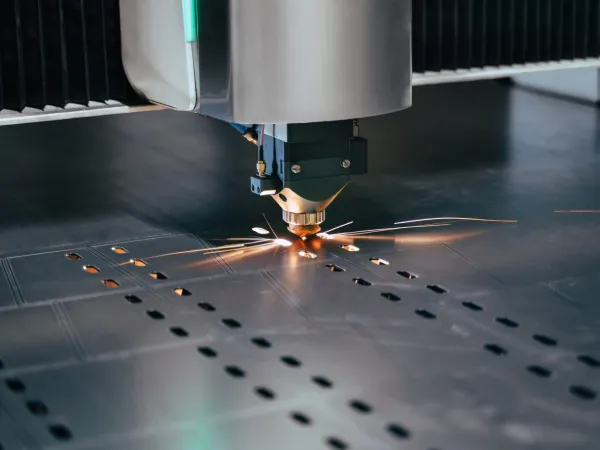
Cutting is the most basic and commonly used fabrication process. This technique involves trimming raw materials, generally metals and plastics, finely to a specific shape and size. In the manufacturing world, the cutting process can be performed using other technologies, such as lasers, plasma torches, mechanical saws, or water jets.
Laser cutting is a precise method that uses a focused laser beam to cut the materials. This technique is used when you want to get an accurate cut for complex shapes and intricate patterns. Laser cutting is ideal for components used in industries like automotive, electronics, and aerospace. Whereas, plasma cutting uses ionized gas (plasma) to cut the electrically conductive materials like aluminum or steel. This process is cost-effective as compared to laser cutting. However, it is less precise. The vast manufacturing industry sometimes uses waterjet cutting fabrication techniques to cut through materials like glass, stone, or metals. It is done by using a high-pressure stream of water mixed with an abrasive substance. The best aspect of this technique is that it doesn’t generate heat, minimizing the risk of deforming sensitive materials.
2.) Welding
Industries dealing with metal structures widely use fabrication in manufacturing. This process involves joining two or more pieces of metal by applying pressure or heat. Sometimes, the combination of pressure and heat is applied by fusing them into a single entity.
Arc welding uses an electrical arc to melt the metals. This creates a molten pool that cools to form a strong bond. This technique is commonly used in the construction of ships, bridges, and pipelines.
Metal Inert Gas (MIG) and Tungsten Inert Gas (TIG) are two variations of arc welding. MIG welding is faster and more suited for thicker metals, while TIG welding is ideal for more precision and is preferred for thinner or more complex welds.
This fabrication process creates durable structures and components for industries like construction, aerospace, and automotive.
3.) Forming
In this fabrication technique, raw materials are reshaped without adding or removing materials. The reshaping is often done by applying force and the material is typically in a ductile or malleable state. The state of the material makes it easier to stretch, bend, or compress. Forging and stamping are two forming techniques commonly used.
In forging, compressive forces are used to shape the metals. This process can be performed hot or cold, majorly depending on the metal’s properties and the required outcome. Forged parts often come out to be stronger as compared to machined components and are widely used in the automotive and aerospace sectors.
Stamping is highly preferred in sheet metal fabrication. This process involves pressing metal sheets into a die to create a specific shape or pattern. It is efficient for mass production and is used for producing car parts, electronic components, and appliances.
4.) Machining
The most precise fabrication process is machining, involving removing material from a workpiece to achieve the desired shape or surface finish. This process can either be performed manually or through automation such as CNC (Computer Numerical Control) machining. Depending on the desired component, machining can be performed using three techniques.
Milling in the machining process where a rotating cutting tool removes material from a workpiece. It is used for creating complex shapes, holes, threads, and slots. This process is versatile and can be performed on plastics, metals, and wood.
In turning, the workpiece is rotated while a cutting tool is applied to remove the material. This technique is perfect and is often used for creating cylindrical parts such as bolts, screws, and shafts.
Lastly, drilling is a machining process that is used to create round holes in a workpiece. It’s an essential step in many fabrication processes, often used along with other machining techniques.
The machining fabrication process ensures that the components meet exact requirements and tolerances.
5.) Casting
In casting, molten material is poured into a hollow mold or die to create a specific shape. Once the metal cools down and solidifies, it takes the shape of the mold, producing the desired component. The common castings are, gravity die casting, pressure die casting, and sand casting. This process is versatile and cost-effective, producing complex shapes and large quantities of parts.
In today’s evolving manufacturing landscape, having a clear understanding of fabrication processes ensures accuracy, efficiency, and innovation.




