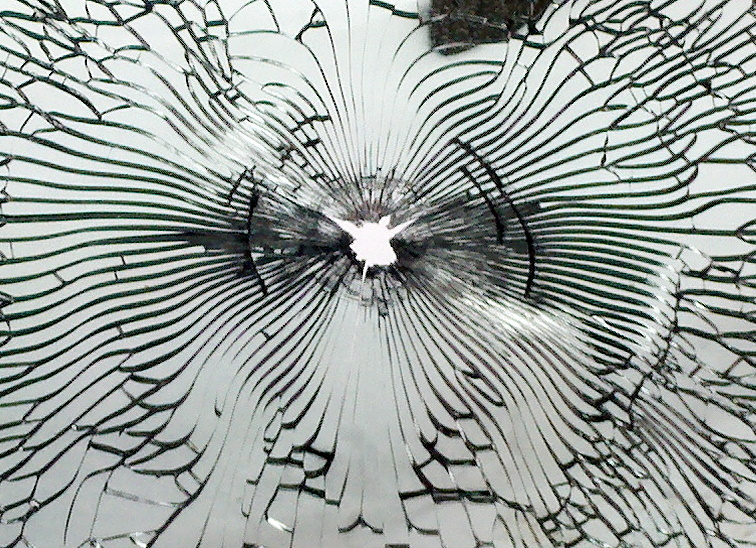
Glass failures rarely happen without warning. A sudden crack, a shattered panel, or an unexplained failure often points to deeper structural or material stress. When breakage glass incidents appear minor, they still raise concerns about safety, liability, and long-term facade performance. Ignoring these signs can lead to repeated failures or costly replacements.
This post explains why glass breaks in buildings, how professionals identify the real cause, and how masterful facade services resolve the issue at its source. The focus stays on practical insight, forensic accuracy, and real-world building conditions, confirming the right place for those seeking clarity rather than guesswork.
Understanding Why Architectural Glass Fails
Glass appears rigid and permanent, yet it constantly reacts to pressure, temperature, and movement. Most failures trace back to stress accumulation rather than sudden impact.
Stress Hidden Inside the Panel
Every glass pane carries internal stress from manufacturing, handling, and installation. When that stress exceeds tolerance, a glass fracture forms. This fracture may spread slowly over weeks or fail instantly under the right trigger.
Common stress contributors include:
- Uneven edge support
- Point loading from anchors or brackets
- Minor chips were introduced during installation
Specialists trained in forensic evaluation, such as teams at Facade Consultants, often identify stress origins by examining crack patterns and edge conditions rather than focusing solely on surface damage.
Envronmental Forces That Trigger Glass Breakage
External conditions play a larger role in glass failures than many building owners expect.
Thermal Expansion and Temperature Swings
Glass expands and contracts with temperature. When shading, coatings, or framing restrict movement, tension builds rapidly. This condition explains many cases of broken glass in curtain walls exposed to uneven sunlight.
Key risk factors include:
- Dark spandrel panels next to clear vision glass
- Partial shading from nearby structures
- Inconsistent glazing thickness across elevations
Thermal stress fractures usually show clean, straight cracks extending from the edge toward the center.
Wind Load and Structural Movement
Buildings move. Wind sway, seismic activity, and live loads shift frames subtly but continuously. If the glazing system lacks tolerance for movement, the glass absorbs that stress. Professionals providing expert facade services assess whether the glass failed due to excessive deflection rather than material weakness. Structural movement often leaves telltale diagonal cracking patterns tied to frame distortion.
Manufacturing and Material Defects
Not all glass failures start on the job site. Some originate in the factory.
Nickel Sulfide Inclusions
Tempered glass occasionally contains microscopic nickel sulfide particles. Over time, these particles expand, triggering spontaneous glass fracture without external force.
Indicators of this issue include:
- Sudden failure without impact marks
- Small butterfly-shaped fragments at the origin
- Breakage occurring years after installation
Experienced forensic consultants, including groups like Facade Consultants, differentiate inclusion-related failures from installation errors through fragment analysis.
Improper Heat Treatment
Incorrect tempering or heat strengthening leads to uneven stress distribution within the material, creating conditions commonly associated with broken glass. This structural flaw weakens the glass and significantly reduces its resistance to thermal or mechanical loads. When on-site evidence is insufficient or inconclusive, laboratory testing is often used to confirm the presence of this defect.
Installation Errors That Compromise Glass Integrity
Installation quality directly affects glass lifespan. Even premium materials fail when installed incorrectly.
Edge Damage During Handling
Glass edges remain the most vulnerable area. Minor chips invisible to the naked eye can grow into a full glass fracture under normal service conditions.
Frequent installation-related risks include:
- Metal-to-glass contact
- Over-tightened fasteners
- Inadequate setting blocks
Specialists offering expert facade services focus heavily on edge inspection, as this area reveals whether damage occurred before or during placement.
Incompatible Framing Systems
Glass must work in harmony with its frame. Mismatched tolerances, rigid anchors, or incorrect gasket materials transfer stress directly into the pane. Consultants like Facade Consultants often identify incompatibility issues by reviewing shop drawings, mock-up testing data, and as-built conditions side by side.
How Experts Diagnose Glass Failures
Professional evaluation follows a structured process rather than assumptions.
Visual and Pattern Analysis
Crack direction, origin point, and fragmentation style provide critical clues. Each glass fracture tells a story through its geometry.
Experts examine:
- Crack initiation zones
- Edge condition under magnification
- Fragment size and distribution
Testing and Simulation
When field evidence requires validation, experts use controlled testing to replicate conditions. Thermal modeling, load simulation, and material testing clarify whether the failure stemmed from design, material, or installation. Firms delivering expert facade services rely on testing data to support corrective strategies rather than relying on visual judgment alone.
Proven Methods to Fix and Prevent Glass Breakage
Repairing a broken panel solves the symptom. Preventing recurrence solves the problem.
Targeted Glass Replacement
Replacement works only when experts address the root cause. This may involve changing glass thickness, coating type, or edge treatment rather than reinstalling the same specification.
System Adjustments and Retrofits
Effective fixes often include:
- Adding movement tolerance within framing
- Adjusting anchor placement
- Updating gasket materials
Facade Consultants and similar specialists frequently recommend system-level adjustments when repeated broken-glass incidents occur within the same elevation or building zone.
Design and Specification Review
Long-term prevention begins with design accountability. Reviewing specifications against actual building conditions ensures the glass system aligns with environmental exposure and structural movement.
Legal and Safety Implications of Glass Failures
Glass failures raise more than maintenance concerns. They affect occupant safety, insurance coverage, and liability exposure. When injuries or property damage occur, expert facade services provide documented analysis that clarifies responsibility. Consultants with forensic experience, like Facade Consultants, often support legal teams by explaining failure mechanisms in clear, defensible terms.
The Bottom Line
Glass breakage usually results from hidden stress, environmental forces, material defects, or installation errors. To identify the true cause of fractures, technical insight and expertise are essential. Properly addressing glass fracture issues enhances safety and prevents future failures.
Buildings benefit from experienced professionals who evaluate the entire facade system rather than just individual components. Property owners, architects, and contractors achieve long-term reliability by choosing experts focused on prevention and repair, ultimately reducing risk, cost, and disruption.